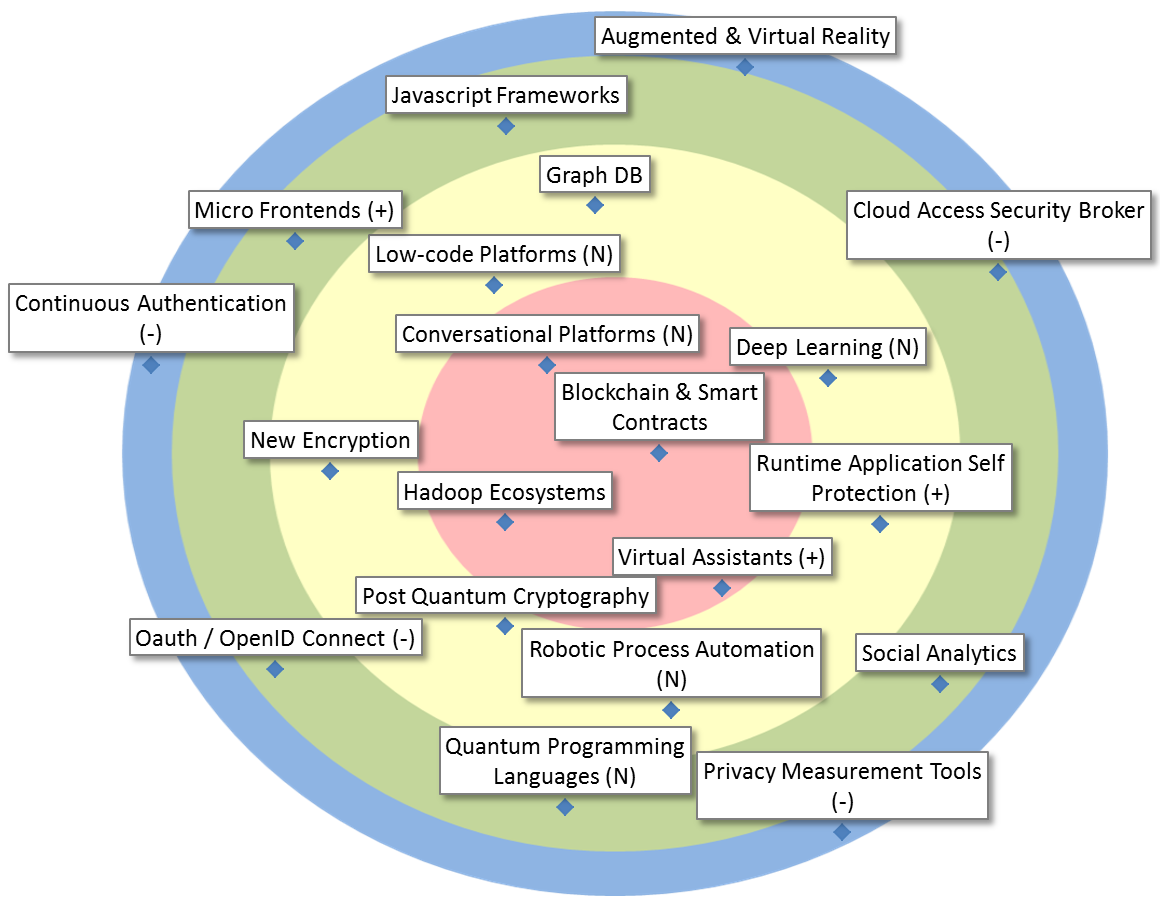
| Blockchain & Smart Contracts |
Blockchain & smart contracts offer autonomous (shared) storage and autonomous computation in a network. Hence, no one can change the data or influence the computation. This offers new possibilities for distributed trust and to simplify existing applications & architectures. |
| Conversational Platforms |
Conversational platforms support the development of conversational interfaces based on intent and entity recognition, context handling, exception handling, messaging platform connectors and monitoring/analytics. |
| Hadoop Ecosystems |
Hadoop Ecosystems implement Big Data distributed storage (HDFS), access (Hive, Impala), distributed computing (MapReduce, Spark), transfer (Sqoop, Kafka, Flume), configuration, monitoring, and management modules, in one integrated environment consisting of several nodes. |
| Virtual Assistants |
Virtual assistants are computer programs that automatically reply to questions or utterances. The basic channel of communication is a conversational interface, that accepts chat or speech. Possible applications are: website guidance, helpdesk assistance, or simplification of procedure. |
| Deep Learning |
Important focus area of AI. Architectures such as Recurrent/Convolutional Neural Nets, GANs, etc. learn hierarchical representations of the data, corresponding to different levels of abstractions, largely from the raw data. Toolkits include TensorFlow, Caffe, Keras,… |
| Graph DB |
Databases based on and/or oriented towards graphs, with nodes (entities) connected through edges (relations). They are very useful in graph analytics, but could also serve in miscellaneous production systems. |
| Low-code Platforms |
Platforms or frameworks on which developers, and sometimes also business stakeholders, can more rapidly build applications. Delivered through PaaS or as libraries, they are often characterized by the use of graphical programming methods, for GUI but also for the logic. |
| New Encryption |
Cryptography is a powerful toolbox but awareness of its potential is yet small. Examples are elliptic curve cryptography (as an alternative to RSA), format preserving encryption, authentic encryption and ring signatures. |
| Post Quantum Cryptography |
Cryptographic algorithms thought to be secure against an attack performed by a quantum computer. |
Robotic Process Automation
|
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology focused on the automation of clerical work, at or near the user interface level, allowing a combination of tasks in different tools and across services, without requiring a deeper integration of these. |
| Runtime Application Self Protection |
Runtime Application Self Protection (RASP) is a security technology that is built or linked into an application or application runtime environment, and is capable of controlling application execution and detecting and preventing real-time attacks. |
| Cloud Access Security Broker |
On-premises or cloud-based security policy enforcement point, placed between cloud service consumers and cloud service providers to combine and interject enterprise security policies as the cloud-based resources are accessed. |
| Javascript Frameworks |
JavaScript has become the most important language on the web (even on the server), and new, powerful frameworks continually evolve to give developers more effective options for web development. |
| Micro Frontends |
In analogy with microservices on the server side, micro front-ends allow the piecemeal development and deployment of an end-user application. The success of this technology will be determined by the quality of the frameworks/platforms combining these ‘pieces’. |
| Oauth / OpenID Connect |
Standards for authentication / authorization relevant in the domains of mobile applications and REST architectures. |
| Quantum Programming Languages |
Quantum programming languages help express quantum algorithms using high-level constructs. This can be used, for instance, to retrieve secret cryptograpahic keys. Recently (dec. 2017), Microsoft introduced Q#. |
| Social Analytics |
The automatic processing and analysis of data from internal and external social media to extract useful information. Most of Big Data Analytics solutions have connectors to exploit these kinds of resources. |
| Augmented & Virtual Reality |
UI technologies offering an immersive experience, using altered or completely simulated environments in which the users senses virtual entities. Hyped in 2016/2017, yet deployment options in the public sector are not readily apparent. Potential uses in (explorational) Analytics. |
| Continuous Authentication |
Methods for continuous verification whether the same specific person who logged into a device is still using it. |
| Privacy Measurement Tools |
Such tools would allow citizens to be informed about the state of their privacy by a simple number or a set of numbers. A related challenge is assessing the impact of a certain query on the citizen’s privacy. This problem is hard and research is mainly at the academic level. |